Graphene the best material to convert heat to electricity
Graphene the best material to convert heat to electricity
American researchers from the University of Groningen and researchers the University of Manchester in England test the Peltier effect in graphene, The Peltier effect is an example of Thermoelectrics: is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, it creates a temperature difference.
At the atomic scale, an applied temperature gradient causes charge carriers in the material to diffuse from the hot side to the cold side.
Researchers study that deals with situations in which a temperature difference creates an electric potential or vice versa. In this effect, a temperature difference appears when a voltage is applied between two electrodes connected to a semiconductor material. The team unambiguously showed that the effect can be switched from heating to cooling by tuning the type and density of the charge carriers inside the material.
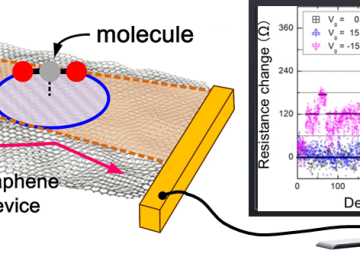
They used graphene because of its 2D nature, and graphene is a wonderful candidate for demonstrating a fully tune-able Peltier effect. The electrical contacts to graphene allowed to electrically control the cooling and heating via the Peltier effect, and to detect this cooling and heating, the researchers constructed sensitive nanoscale thermometers that directly measured the temperature of electrons in graphene. This practical approach is said to be the first of its kind for 2D materials, and its sensitivity is a thousand times better than that of its predecessors, down to 0.1 milliKelvin.
Thermoelectrics can play a significant role in heat managing and in generating electrical energy from wasted heat. The emerging family of 2D materials, like graphene, offers exciting opportunities because it’s relatively easy to tune their thermoelectric properties. Therefore, the scientific interest in the interaction between charge and heat in such materials opens the door to both novel fundamental studies, and can help realize more sustainable electronics.